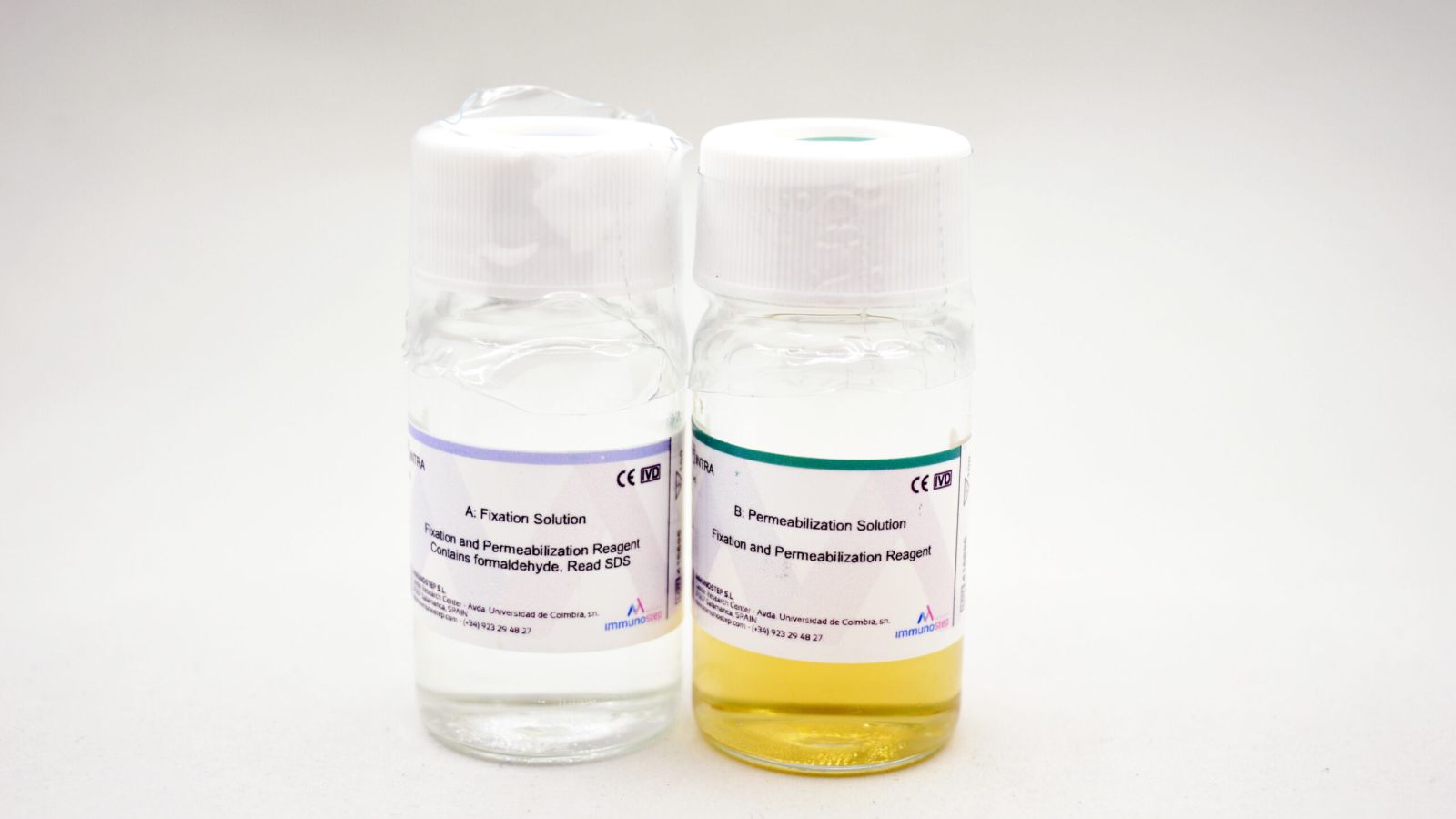
In biomedical research and advanced diagnostics, the conjugation of fluorochromes to proteins plays a key role in the accurate detection of biomolecules. Two essential reagents in these assays are FITC-Streptavidin...
INTRACELL: Analysis of autophagy and apoptosis on a single platform
In the field of biomedical research, understanding the mechanisms of cell death and survival is essential to develop new therapies and diagnostic strategies. One of the major challenges in this field...
Customized peptide and protein synthesis services: driving scientific research forward
In the field of biotechnology and biomedical research, the availability of customized peptide and proteins is essential for the development of targeted studies and innovative applications.
Immunostep...
Monoclonal Antibodies: Key Tools in Biomedical Research and Diagnostics
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have revolutionized biomedicine since their development in the 1970s, becoming essential tools both in research and in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases.
What...
Importance of Isotype Controls in Cytometry Experiments
In flow cytometry experiments, the accuracy and reliability of the results depend largely on correctly interpreting the fluorescent signal. It is crucial to distinguish between the specific signal,...
Apoptosis Detection with Immunostep: Advanced Tools for Cellular Research
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is an essential process in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and embryonic development. Its deregulation is implicated in several pathologies, such as neurodegenerative...
What is Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria and how to treat it?
Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired and potentially severe haematological disease characterised by red blood cell destruction, thrombosis and bone marrow dysfunction. Its...
FlowBoScan™ vs. ToBoScan™: Which is the Better Choice for Monocyte and Macrophage Detection?
In the field of immunology and oncology research, accurate identification of monocytes and macrophages is essential for understanding various pathologies and developing effective therapies. To address...
BasoStep: Advanced Basophil Activation Test for Allergy Diagnosis
In allergy diagnostics, flow cytometry has revolutionized the detection and study of allergic reactions. Among these innovations, Immunostep’s BasoStep kit plays a key role in evaluating IgE-mediated...
Capture and characterisation of exosomes with CD9 capture beads in neurodegenerative diseases
Exosomes have emerged as a key field of study in biotechnology and medicine, with applications in diagnostics, therapy and disease monitoring. However, their isolation and characterisation remain major...