- Products
- Oncohematology
- Antibodies
- Kits
- CAR T-cell
- Euroflow
- Single reagents
- Request info
- Resources and support
- Immunology
- Antibodies
- Single reagents
- Cross match determination (FCXM)
- FcεR1
- Ig subclasses
- Single reagents
- Kits
- TiMas, assessment of tissue macrophages
- Request info
- Resources and support
- Antibodies
- Exosomes
- Accesory reagents
- Software
- Oncohematology
- Services
- Peptide Production
- Design
- Modification
- Protein Services
- Expression and purification
- Freeze drying
- Monoclonal And Polyclonal Antibody Development
- Monoclonal
- Policlonal
- Specialized antibody services
- OEM/Bulk production
- Purification
- Conjugation
- Custom Exosome Services
- Isolation and purification
- Characterization
- Peptide Production
- Shop
- Support
- About Us
- Contact
ThromboStep:
Diagnostic kit designed to quantify platelet associated immunoglobulin using Flow Cytometry
This kit contains:
-
An R-phycoerythrin (R-PE) conjugated monoclonal antibody, which recognizes a platelet specific antigen;
-
Polyclonal antibodies conjugated whit fluoresce in isothiocyanate (FITC) against total human immunoglobulins, human IgA, IgM, and IgG;
-
A polyclonal antibody conjugated whit FITC as a negative control.
-
Two bottles of 10X ammonium oxalate (25 ml) with simple instructions for preparing the 1X solution in distilled water.
Highly sensitive assay for platelet autoantibody detection
Platelet autoantibody detection is critical for immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) diagnosis and prognosis, and that is the reason why we will need an assay for the quantification of platelet-associated immunoglobulins. ThromboStep kit provides a highly sensitive assay with this purpose, using Flow Cytometry.
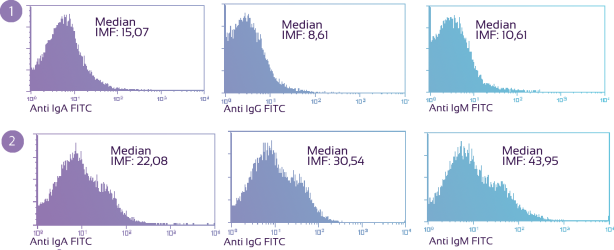
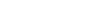
Figure 1: Immune Thrombocytopenia. The histograms represent comparison of a healthy control sample (1) and immune thrombocytopenia sample (2).
Immune Thrombocytopenia
Normal human platelet counts range from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microlitre of blood. Thrombocytopenia is the presence of too few platelets.
Decreased platelet counts may be due to different pathological processes, however, quantification of platelets associated with immunoglobulins allows the cause of thrombocytopenia to be related to a decrease in platelet production or an increase in the rate of platelet destruction.
Highly specific evaluation of thrombocytopenia
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) is an autoimmune disorder characterised by a low platelet count and mucocutaneous bleeding. The autoantibodies are directed primarily to the platelet-specific receptors CD41a (GPIIb/IIIa) and CD42b (GPIb).
As a result, the sensitized platelets are rapidly cleared by the monocyte-macrophage cell systems. The determination of autoantibodies against thrombocytes allows differentiate immune from nonimmune thrombocytopenia.
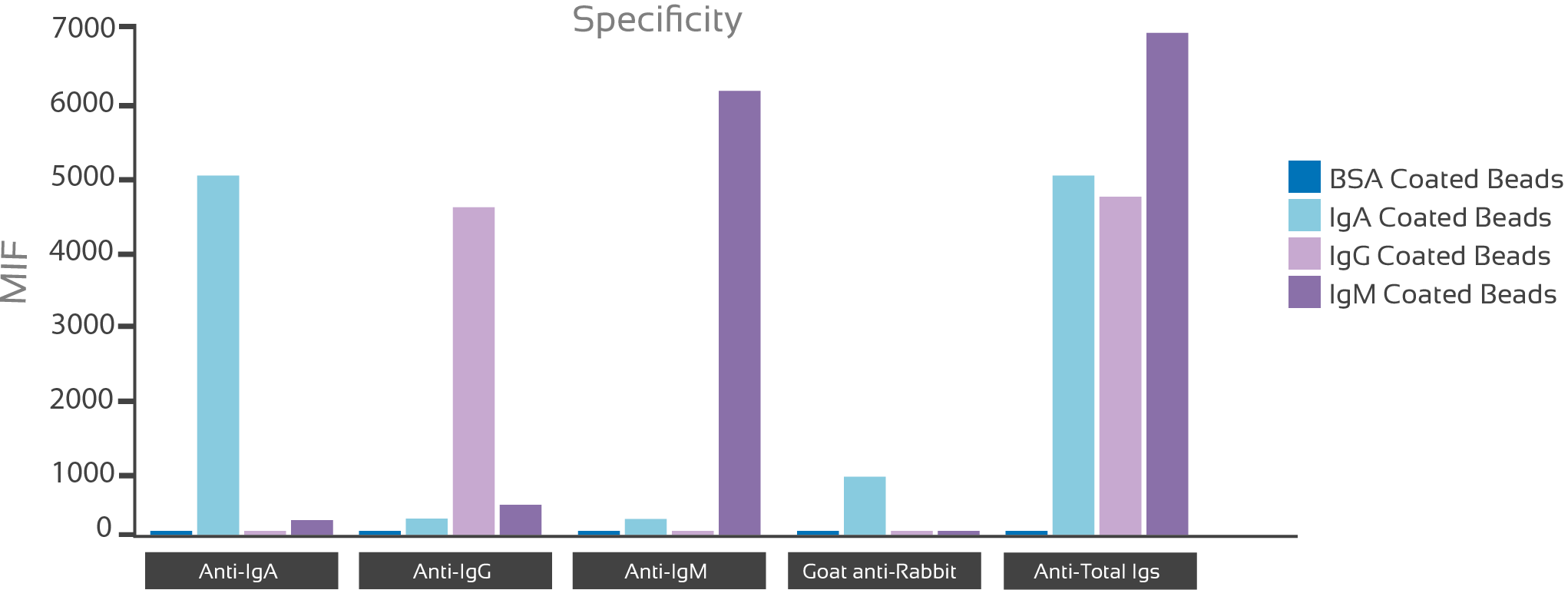
Figure 2: kit specificity assessment. Anti-human Igs were incubated respectively with human immunoglobulins IgA, IgG and IgM and BSA (control) coated polystyrene beads.
Anti-human Igs specificity analysis shows a very low cross-reactivity (>7%) for all of them, making easy the correct identification of non-pathological sample.
PRODUCT REFERENCES
| Product Reference | Description | |
|---|---|---|
TBS | ThromboStep Kit | 50 test | Download TDS | GO TO SHOP |